The BEST
Analyzer Solution
for Monitoring Water
Contact Us



Benefits
The INSTRAN online analyzer is the best solution to measure and control different physical and chemical parameters in aqueous solutions, such as drinking water or wastewater, facilitating the control of the configured parameter, automating plant processes and achieving system optimization.
Accuracy
Accuracy, repeatability and reliabilityLow maintenance
Low maintenance required due to Instran designAutonomy
Low consumption of reagents to increase autonomyRobustness
Robustness thanks to spares are manufactured by the best materialsAdaptable
Auto-cleanings available to adapt the analyzer to waste water samples

What is Instran®?
Reduces the operational cost
INSTRAN ® is designed with the best and more resistant materials against aggressive chemical reagents as hydrochloric acid, caustic soda, etc. used to perform chemical reactions. Its optimal design, by experts with more than 30 years of experience on the field of online analysis and water quality, protects the critical mechanical spares, prolonging the shelf-life of them, and subsequently, the analyzer shelf-life too. It also implies that the analyzer maintenance is reduced. At the same time, the size and design of the reaction cell, reduces the consumption of reagents without it could affect the sensitive and accuracy of the measurement. All these features reduces the operational cost, which sometimes is extremely higher than the main analyzer price.
Accuracy up to 0.015ml drop
The exceptional and innovative dose system used by INSTRAN permits an accuracy up to 0.015ml drop, solving one of the critical parameters in online analysis and eliminating at all the several inconveniences created by the common peristaltic pumps.
Unique versatility
Instrumentación Analitica SA wrote and manages the analyzer software. It makes possible that the analyzer can be adapted to unusual sample conditions and difficult applications, according to customer needs. Thanks also to IA engineers high knowledge and suggestions, provides a unique versatility to the client.
All these features makes INSTRAN ® provides a very accurate and reliable result, being the best available option in the market to control water quality.
Features
| Environmental conditions | 0ºC to 45ºC |
|---|---|
| Power | Input: AC 100-240 V — 50 Hz Max. power: 288 W |
| Set up | Steel frame IP66 enclosure |
| Size | Steel frame: 65x40x15 cm IP66 enclosure: 75x55x30 cm |
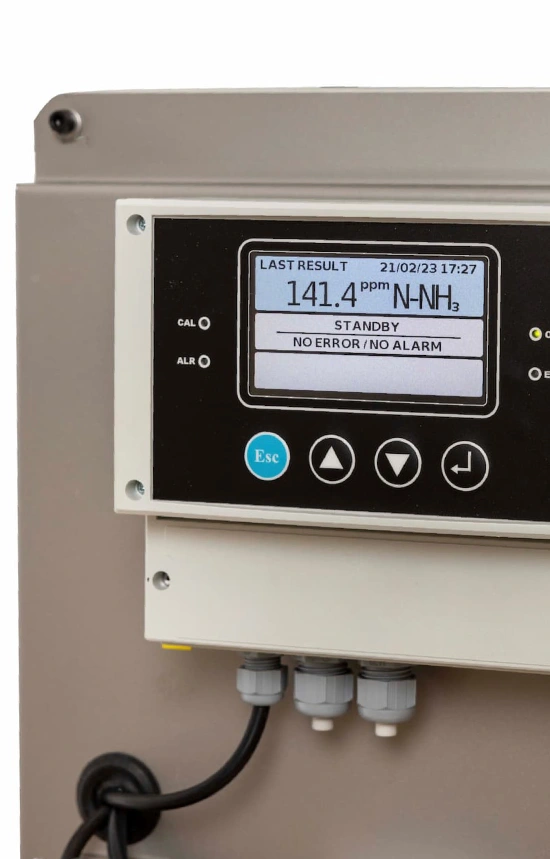
| User interface | Keypad with 4 keys and 4 indication LEDs |
| Languages | English, Spanish |
| Communications | 4-20 mA signal RS-485 communication RS485 MODBUS or PROFIBUS |
| Relays | 4 Relays (24V), assigned by user |
| Diagnostic menu | Self-evaluation of analyzer status |
| Calibration | Manual or automatic |
| Analysis | Manual or automatic |
| Cleanings | Scheduled cleanings before and after each analysis with sample, DIW or specific solution |
|---|---|
| Analysis corrections | Temperature correction Blank correction LED current correction |
| Dose system | Syringe driven by step by step motor. Accuracy: 0.015 ml |
| Fluid system | Loop to protect the syringe Valves made of Kalrez® High resistance tubing (Tygon 2375) Complete system without fittings |
| Reaction Vessel | Low volume glass vessel (17ml) Automatic system to prevent overflow Special design to make drain easier |
| Fluid system | Inlet: 6 mm tub Outlet: 8 mm tub Fast loop inlet Sample level detector Anti-overflow system Manual valve to drain while manual cleaning |
Parameters
Contact Us-
Method – Titration
After adding the reagents to establish the desirable conditions to the sample, the volume of titrant is charged. Thanks to the module syringe driver minimum dose (0.015 ml), the accuracy achieved is really high, with 3 drops differences as much between 2 consecutives analysis of the same standard. Moreover, the software has been improved to speed up the initial dose, whereas when the inflection point is close, the titrant is added slowly, to achieve precision.
Principle of measurement
The sample is titrated with hydrochloric acid to a colorimetric end point corresponding to a specific pH. Phenolphthalein alkalinity is determined by titration to a pH of 8.3, as evidenced by the color change of phenolphthalein indicator, and indicates the total hydroxide and one half the carbonate present.
Advantages of the method
The method is specific for alkalinity, and thanks to the accuracy of the system of Instran the repeatability achieved is really high.
Interferences of the method
Highly colored or turbid samples may mask the color change at the end point.
Specifications
- Range: From 0 to 100 ppm / 250 ppm / 500 ppm / 1000ppm. Adjustable to lower/higher concentrations
- Accuracy: 2%
- Repeatability: 2%
- Resolution: 0,01 ppm or 0,1 ppm
- Analysis time: around 20 minutes
- Calibration: one point
- LED Wavelength: 625 nm
- Reagents consumption:
- Reagent 1: 1ml / analysis – 0.75L / month (1 analysis per hour)
- Titrant: 4ml / analysis – 3L / month (1 analysis per hour)
- Monthly volume calculated assuming 1 analysis per hour.
-
Method – Colorimetric
After adding the sample into the measurement cell, some reagents are added in order to adjust the solution to the desired conditions (pH, valence’s elements, etc.). Then, a blank is done to correct any temperature or turbidity disturbance. Subsequently, a last reagent is added, and it reacts with solution developing a color, which is measured using a correct wavelength. Thanks to the photometer used, the result achieves a great accuracy.
Principle of measurement
The method is based upon that used by the South West Water Authority. It uses the hydroxylamine hydrochloride to reduce iron to the ferrous state and complexes it with 1,10-phenantroline. The aluminum is then complexed with the pyrocatechol violet.
Advantages of the method
The method is specific for the measurement of aluminum once any iron has been complexed by the addition of the 1,10-phenanthroline-hydroxyammonium chloride.
Interferences
Fluoride, phosphate, detergents, chromium
Specifications
- Range: From 0 to 200 ppb / 500 ppb. Adjustable higher concentrations with internal dilution.
- Resolution: 2%
- Repeatability: 2%
- Analysis time: around 15 minutes
- Calibration: two point
- LED Wavelength: 588 nm
- Reagents consumption:
- Reagent 1: 0.6 ml / analysis – 0.5L / month
- Reagent 2: 3 ml / analysis – 2.25L / month
- Monthly consumption calculated assuming 1 analysis per hour.
-
Method – ISE
The standard known addition (SKA) technique is used to perform the analysis. During the process, two readings are done. The difference between both and the slope found during calibration are used to calculate the concentration. Possible changes on the matrix sample are corrected due to this both lectures, as the reference to calculate the result is the relative difference of mV and not the absolute values. This avoids external interferences.
Principle of measurement
The sodium hydroxide solution as well as acting as an ionic strength adjuster neutralizes the solution to ensure that all the ammonium ion is present as ammonia. The addition of the SKA solution providing a known added concentration of ammonium ion allows the current Eo to be calculated. The difference between this value of the potential and the first potential value measured is used to calculate the concentration of ammonia in the sample solution.
Advantages of the method
The method is very simple and is fairly specific as the ammonium electrode has little cross interference from other ions. Moreover, how the result is based on the difference of mV, any change on the matrix sample is corrected. It can be used with brine up to 300 g/L of NaCl.
Specifications
- Range: From 0 to 0.5ppm / 2ppm / 5ppm / 20ppm / 100ppm. Adjustable higher concentrations with internal dilution.
- Accuracy: 2%
- Resolution: 2%
- Analysis time: around 10 minutes
- Calibration: one point
- ISE: Ammonia NH3 electrode
- Reagents consumption:
- Reagent 1: 0.5 ml / analysis – 0.5L / month
- Reagent 2: 0.5 ml / analysis – 0.5L / month
- Monthly consumption calculated assuming 1 analysis per hour.
-
Method – ISE Titration
After adding the reagents to establish the desirable conditions to the sample, the volume of titrant is charged. Thanks to the module syringe driver minimum dose (0.015 ml), the accuracy achieved is really high, with 4 drops differences as much between 2 consecutives analysis of the same standard. Moreover, the software has been improved to speed up the initial dose, whereas when the inflection point is close, the titrant is added slowly, to achieve precision.
Principle of measurement
Boric acid is a very weak acid and direct titration with NaOH is not possible. However, addition of Mannitol-D makes a significant and visual end point determination, based on the change of pH on the sample.
Advantages of the method
The method is specific for the measurement of boron. The 6000 steps motor that controls the syringe movement allows to dose really small drops, getting accuracy and repeatable results. Moreover, the reagents are simple to be prepared and cheap. Changing the concentrations of reagents, the range of measurement is easily modifiable.
Specifications
- Range: From 0 to 50 ppm / 100 ppm / 250 ppm / 500 ppm. Adjustable higher concentrations adjusting reagents concentrations.
- Accuracy: 2% Full Scale
- Repeatability: 2%
- Resolution: 0,01 ppm or 0,1 ppm
- Analysis time: around 15 minutes
- Calibration: one point
- ISE: pH electrode
- Reagents consumption:
- Reagent 1: 4.0 ml / analysis – 3 L / month
- Reagent 2: 4.5 ml / analysis – 3.5 L / month
- Monthly consumption calculated assuming 1 analysis per hour.
-
Method – Colorimetric
After adding the sample into the measurement cell, some reagents are added in order to adjust the solution to the desired conditions (pH, valence’s elements, etc.). Then, a blank is done to correct any temperature or turbidity disturbance. Subsequently, a last reagent is added, and it reacts with solution developing a color, which is measured using a correct wavelength. Thanks to the photometer used, the result achieves a great accuracy.
Principle of measurement
Thanks the buffer reagent, the sample is adjusted to pH between 5 and 6. Then, the addition of Azomethine-H & Ascorbic acid, they react with Boron giving a green-yellow color that is measured at 420nm.
Advantages of the method
The method is accurate and sensitive. The range is linear up to 2 ppm and higher ranges can be obtained diluting the sample.
Specifications
- Range: From 0 to 100 ppb / 500 ppb / 1000 ppb / 2000 ppb. Adjustable higher concentrations adjusting reagents concentrations.
- Accuracy: 2%
- Repeatability: 2%
- Resolution: 0,1 ppb
- Analysis time: around 30 minutes
- Calibration: two point
- LED Wavelength: 420 nm
- Reagents consumption:
- Reagent 1: 2.20 ml / analysis – 2 L / month
- Reagent 2: 4.20 ml / analysis – 3.5 L / month
- Monthly consumption calculated assuming 1 analysis per hour.
-
Method – Titration
After adding the reagents to establish the desirable conditions to the sample, the volume of titrant is charged. Thanks to the module syringe driver minimum dose (0.015 ml), the accuracy achieved is really high, with 3 drops differences as much between 2 consecutives analysis of the same standard. Moreover, the software has been improved to speed up the initial dose, whereas when the inflection point is close, the titrant is added slowly, to achieve precision.
Principle of measurement
This method is a modification of the method developed by Reilly, Anal. Chem. The pH of the solution ensures that the magnesium is precipitated and hence is not titrated.
Advantages of the method
The method is specific for calcium even in the presence of excessive amounts of magnesium. As the measurement wavelength is centered on the Ca-Calcon complex and the reference wavelength is centered on the EDTA-Calcon complex, the end-point is both accurately and reproducibly measured.
Specifications
- Range: From 0 to 50 ppm /100 ppm/ 250ppm / 500 ppm/ 1000 ppm. Adjustable to lower/higher concentrations
- Accuracy: 2%
- Repeatability: 2%
- Resolution: 0,1 ppm
- Analysis time: around 20 minutes
- Calibration: one point
- LED Wavelength: 625 nm
- Reagents consumption:
- Reagent 1: 0.15 ml / analysis – 0.125L / month
- Reagent 2: 3 ml / analysis – 2.25L / month
- Titrant: 4 ml / analysis – 3.0L / month
- Monthly volume calculated assuming 1 analysis per hour.
-
Method – ISE
The standard known addition (SKA) technique is used to perform the analysis. During the process, two readings are done. The difference between both and the slope found during calibration are used to calculate the concentration. Possible changes on the matrix sample are corrected due to this both lectures, as the reference to calculate the result is the relative difference of mV and not the absolute values. This avoids external interferences.
Principle of measurement
Reagent 1 is added to activate the electrode before the analysis. After that, a first measurement is done. Subsequently, a small volume of a high concentrated nitrate solution is added. Finally, a second lecture of mV takes place to calculate the result.
Advantages of the method
The method is very simple and is fairly specific as the chloride measurement and just a few parameters cause interferences, which can be removed.
Specifications
- Range: From 0 to 5ppm / 20ppm / 50ppm / 100ppm / 500ppm. Adjustable higher concentrations
- AcCuracy: ±2%
- Repeatability: ±2%Resolution: 0,01 ppm / 0,1 ppm / 1 ppm
- Analysis time: around 10 minutes
- Calibration: one point
- ISE: Chloride Cl- electrode
- Reagents consumption:
- Reagent 1: 0.5 ml / analysis – 0.5L / month
- Reagent 2: 0.5 ml / analysis – 0.5L / month
- Monthly consumption calculated assuming 1 analysis per hour.
-
Method – ISE
The standard known addition (SKA) technique is used to perform the analysis. During the process, two readings are done. The difference between both and the slope found during calibration are used to calculate the concentration. Possible changes on the matrix sample are corrected due to this both lectures, as the reference to calculate the result is the relative difference of mV and not the absolute values. This avoids external interferences.
Principle of measurement
Actually, the method is based on the measurement of iodide. Thanks to the reaction between chlorine, the buffer and potassium iodide reagent, chlorine reacts with potassium and iodide is released. Chlorine displaces the iodide. Then, the electrode measures iodide and the amount of iodide measured is equivalent to the chlorine in sample.
Advantages of the method
The method is very simple and specific to measure chlorine. The consumption of reagents is fairly low. Chromate ion, which is an interference for the amperometric method, it is not an interference. Conductivity and calcium, important interferences in DPD methods, are not an interference.
Interferences
Strong oxidizing agents that can convert iodide to iodine, including iodate, bromine, cupric ion, and manganese dioxide, interfere with the method. Silver and mercuric ions must be below about 10 to 20 ppm.
Specifications
- Range: From 0 to 1ppm / 5ppm / 20ppm. Adjustable higher concentrations
- Accuracy: ±2%
- Repeatability: ±2%
- Resolution: 0,01 ppm
- Analysis time: around 10 minutes
- Calibration: two points
- ISE: Chlorine electrode
- Reagents consumption:
- Reagent 1: 0.5 ml / analysis – 0.5L / month
- Reagent 2: 0.5 ml / analysis – 0.5L / month
- Monthly consumption calculated assuming 1 analysis per hour.
-
Method – Colorimetric
After adding the sample into the measurement cell, some reagents are added in order to adjust the solution to the desired conditions (pH, valence’s elements, etc.). Then, a blank is done to correct any temperature or turbidity disturbance. Subsequently, a last reagent is added, and it reacts with solution developing a color, which is measured using a correct wavelength. Thanks to the photometer used, the result achieves a great accuracy.
Principle of measurement
Cerium sulfate is added, which oxidizes the sample and converts all forms of chromium to chromium VI. Then diphenylcarbohydrazide is added which reacts with the chromium VI to produce a reddish-purple color.
Advantages of the method
The method is very simple, very specific and is very sensitive because of the high absorbance of the diphenylcarbazide-chromium(VI) complex formed. Chromium (III) can be measuring calculating the difference between Cr Total and Cr (VI)
Specifications
- Range: From 0 to 200 ppb. Adjustable higher concentrations with internal dilution.
- Accuracy: 2%
- Repeatability: 2%
- Resolution: 0,1 ppb
- Analysis time: around 10 minutes
- Calibration: two point
- LED Wavelength: 545 nm
- Reagents consumption:
- Reagent 1: 2.5 ml / analysis – 2.00L / month
- Reagent 2: 0.8 ml / analysis – 0.75L / month
- Monthly consumption calculated assuming 1 analysis per hour.
-
Method – Colorimetric
After adding the sample into the measurement cell, some reagents are added in order to adjust the solution to the desired conditions (pH, valence’s elements, etc.). Then, a blank is done to correct any temperature or turbidity disturbance. Subsequently, a last reagent is added, and it reacts with solution developing a color, which is measured using a correct wavelength. Thanks to the photometer used, the result achieves a great accuracy.
Principle of measurement
The chromium (VI) reacts with the diphenylcarbazide reagent to form a pik complex. The reaction is specific for chromium (VI) and there are no interference compounds.
Advantages of the method
The method is very simple, very specific and is very sensitive because of the high absorbance of the diphenylcarbazide-chromium(VI) complex formed.
Specifications
- Range: From 0 to 200 ppb. Adjustable higher concentrations with internal dilution.
- Accuracy: 2%
- Repeatability: 2%
- Resolution: 0,1 ppb
- Analysis time: around 10 minutes
- Calibration: two point
- LED Wavelength: 545 nm
- Reagents consumption:
- Reagent 1: 0.8 ml / analysis – 0.75L / month
- Monthly consumption calculated assuming 1 analysis per hour.
-
Method – Colorimetric
After adding the sample into the measurement cell, some reagents are added in order to adjust the solution to the desired conditions (pH, valence’s elements, etc.). Then, a blank is done to correct any temperature or turbidity disturbance. Subsequently, a last reagent is added, and it reacts with solution developing a color, which is measured using a correct wavelength. Thanks to the photometer used, the result achieves a great accuracy.
Principle of measurement
The method is based on the formation of melamine-cyanurate, which is not soluble. The turbidity formed is measured subsequently to calculate the concentration. The sample has to be prepared before to determinate pH conditions.
Advantages of the method
The composition of regent 1 makes that the sample is prepared to a specific pH and the powder formed is slight and dispersed, causing higher absorbance. Moreover, the precipitation of melamine-cyanurate is complete and quick. It also works with high concentration of brine (100 g/l).
Specifications
- Range: From 5 to 10 ppm. Adjustable higher concentrations with internal dilution.
- Limit of detection: 4 ppm
- Resolution: 2%
- Repeatability: 2%
- Analysis time: around 15 minutes
- Calibration: two point
- LED Wavelength: 650 nm
- Reagents consumption:
- Reagent 1: 0.66 ml / analysis – 0.5L / month
- Reagent 2: 2.0 ml / analysis – 1.5L / month
- Monthly consumption calculated assuming 1 analysis per hour.
-
Method – Colorimetric
After adding the sample into the measurement cell, some reagents are added in order to adjust the solution to the desired conditions (pH, valence’s elements, etc.). Then, a blank is done to correct any temperature or turbidity disturbance. Subsequently, a last reagent is added, and it reacts with solution developing a color, which is measured using a correct wavelength. Thanks to the photometer used, the result achieves a great accuracy.
Principle of measurement
The method relies upon the reduction of copper(II) to copper(I) in acidic solution. The neocuproine reagents reacts specifically with the cuprous ions. Iron, if present, is also reduced to the ferrous (II) state which would react with the neocuproine.
Advantages of the method
The method is specific for copper and the cuprous(I)-neocuproine complex has such a well-defined and relatively strong absorbance that low ppb levels of copper can be measured using this method. The presence of Iron could be removed with an extra reagent
Specifications
- Range: From 0 to 50 ppb / 250 ppb / 500 ppb / 2ppm. Adjustable higher concentrations with internal dilution.
- Accuracy: ±2%
- Repeatability: ±2%
- Resolution: 0,1 ppb
- Minimum value detection: 2-3 ppb
- Analysis time: around 12 minutes
- Calibration: two point
- LED Wavelength: 450 nm
- Reagents consumption:
- Reagent 1: 1.7 ml / analysis – 1.25L / month
- Reagent 2: 0.7 ml / analysis – 0.50L / month
- Reagent 3: 0.3 ml / analysis – 0.25L / month
- Monthly consumption calculated assuming 1 analysis per hour.
-
Method – Colorimetric
After adding the sample into the measurement cell, some reagents are added in order to adjust the solution to the desired conditions (pH, valence’s elements, etc.). Then, a blank is done to correct any temperature or turbidity disturbance. Subsequently, a last reagent is added, and it reacts with solution developing a color, which is measured using a correct wavelength. Thanks to the photometer used, the result achieves a great accuracy.
Principle of measurement
After adding a buffer to establish the desired pH conditions to reactions takes place, Chloramine-T reagent reacts with cyanide ion to form cyanogen chloride. Afterwards, this compound reacts with the reagent color to form a blue colored complex. The intensity of the blue color developed is proportional to the concentration of cyanide in sample.
Advantages of the method
The sample conditions established before adding the reagents that react with Cyanide permits that the method is specific for cyanide determination. Although the last reaction needs around 25-30 minutes to be finished, a technique used by Instran enables to reduce considerably the analysis time.
Specifications
- Range: From 0 to 200 ppb. Adjustable higher concentrations with internal dilution.
- Accuracy: 2%
- Repeatability: 2%
- Resolution: 0,1 ppb
- Analysis time: around 20 minutes
- Calibration: two point
- LED Wavelength: 588 nm
- Reagents consumption:
- Reagent 1: 1 ml / analysis – 0.75L / month
- Reagent 2: 1 ml / analysis – 0.75L / month
- Reagent 3: 2 ml / analysis – 1.50L / month
- Monthly consumption calculated assuming 1 analysis per hour.
-
Method – ISE
The standard known addition (SKA) technique is used to perform the analysis. During the process, two readings are done. The difference between both and the slope found during calibration are used to calculate the concentration. Possible changes on the matrix sample are corrected due to this both lectures, as the reference to calculate the result is the relative difference of mV and not the absolute values. This avoids external interferences.
Principle of measurement
Conditioning of the sample with TISAB III to adjust pH to 5.5 and eliminate interference
of polyvalent cations. After that, the concentration of fluoride is measured by the method Known Addition (DKA)Advantages of the method
The method is so simple and easy to be performed. It is specific for fluoride, without interferences after addition of TISAB III. Method DKA allows to correct any electrode drifts.
Specifications
- Range: From 0 to 0.5ppm / 2ppm / 5ppm / 20ppm / 100ppm. Adjustable higher concentrations with internal dilution.
- Resolution: 2%
- Repeatability: 2%
- Analysis time: around 10 minutes
- Calibration: one point
- ISE: Fluoride F electrode
- Reagents consumption:
- Reagent 1: 0.5 ml / analysis – 0.5L / month
- Reagent 2: 0.5 ml / analysis – 0.5L / month
- Monthly consumption calculated assuming 1 analysis per hour.
-
Method – Colorimetric
After adding the sample into the measurement cell, some reagents are added in order to adjust the solution to the desired conditions (pH, valence’s elements, etc.). Then, a blank is done to correct any temperature or turbidity disturbance. Subsequently, a last reagent is added, and it reacts with solution developing a color, which is measured using a correct wavelength. Thanks to the photometer used, the result achieves a great accuracy.
Principle of measurement
The calcium and magnesium form a complex with the cresolphthalein complexone, which on adding the buffer, which brings the pH to about 9.6, a characteristic purple complex is formed. If only the calcium is to be measured the magnesium may be complexed.
Advantages of the method
The reagents are exceedingly stable, especially the amine buffer. The method is also extremely sensitive permitting ppb ranges to be measured.
Specifications
- Range: From 0 to / 500 ppb / 1000 ppb / 2 ppm. Adjustable higher concentrations with internal dilution.
- Accuracy: 2%
- Repeatability: 2%
- Resolution: 0,1 ppb
- Analysis time: around 15 minutes
- Calibration: two point
- LED Wavelength: 570 nm
- Reagents consumption:
- Reagent 1: 4.0 ml / analysis – 3.0L / month
- Reagent 2: 1.5 ml / analysis – 1.0L / month
- Reagent 3: 1.5 ml / analysis – 1.0L / month
- Monthly consumption calculated assuming 1 analysis per hour.
-
Method – Titration
After adding the reagents to establish the desirable conditions to the sample, the volume of titrant is charged. Thanks to the module syringe driver minimum dose (0.015 ml), the accuracy achieved is really high, with 3 drops differences as much between 2 consecutives analysis of the same standard. Moreover, the software has been improved to speed up the initial dose, whereas when the inflection point is close, the titrant is added slowly, to achieve precision.
Principle of measurement
The calcium and magnesium complexes with the Erichrome Black-T to give a blue-violet colored complex. This, when titrated by the addition of EDTA, is broken up as the calcium EDTA/ Magnesium EDTA complexes are more stable and when excess EDTA is present the Erichrome Black-T - EDTA complex is formed which is a rose colored complex.
Advantages of the method
The complexometric titration of both the calcium and magnesium, which are the main contributors to the hardness of water, gives a very sharp end point because at the end-point neither the Ca-EBT nor the EDTA-EBT complexes exist.
Specifications
- Range: From 0 to 100 ppm/ 250ppm / 500 ppm/ 1000 ppm. Adjustable to lower/higher concentrations
- Accuracy: 2%
- Repeatability: 2%
- Resolution: 0,1 ppm
- Analysis time: around 20 minutes
- Calibration: one point
- LED Wavelength: 650 nm
- Reagents consumption:
- Reagent 1: 2ml / analysis – 1.5L / month
- Reagent 2: 2ml / analysis – 1.5L / month
- Titrant: 5ml / analysis – 4.5L / month
- Monthly volume calculated assuming 1 analysis per hour.
-
Method – Colorimetric
After adding the sample into the measurement cell, some reagents are added in order to adjust the solution to the desired conditions (pH, valence’s elements, etc.). Then, a blank is done to correct any temperature or turbidity disturbance. Subsequently, a last reagent is added, and it reacts with solution developing a color, which is measured using a correct wavelength. Thanks to the photometer used, the result achieves a great accuracy.
Principle of measurement
There is a direct coupling of the carbonyl group of the 4-aminobenzaaldehyde with the NH2 group of the hydrazine to form a yellow colored complex.
Advantages of the method
The method is very simple requiring but a single reagent, which is specific for hydrazine. Keeping the reagent in an amber container, which will not transmit UV light, the reagent is stable for at least a month.
Specifications
- Range: From 0 to 100 ppb. Adjustable higher concentrations with internal dilution.
- Accuracy: 2%
- Repeatability: 2%
- Resolution: 0,1 ppb
- Analysis time: around 18 minutes
- Calibration: two point
- LED Wavelength: 450 nm
- Reagents consumption:
- Reagent 1: 2.5 ml / analysis – 2.0L / month
- Monthly consumption calculated assuming 1 analysis per hour.
-
Method – Colorimetric
After adding the sample into the measurement cell, some reagents are added in order to adjust the solution to the desired conditions (pH, valence’s elements, etc.). Then, a blank is done to correct any temperature or turbidity disturbance. Subsequently, a last reagent is added, and it reacts with solution developing a color, which is measured using a correct wavelength. Thanks to the photometer used, the result achieves a great accuracy.
Principle of measurement
Any ferric iron is reduced to the ferrous state by means of the hydroxylamine hydrochloride. The ferrous ions react with the 1:10-phenanthroline to form a pink complex when the buffer brings the solution within the range 5 to 7 pH.
Advantages of the method
The method enables iron to be measured at very rather higher levels without resulting in high absorbance values being obtained. The reagents are stable. If total iron has to be measured the stirring time may be increased to ensure that the iron has been completely dissolved by the acidic medium.
Specifications
- Range: From 0 to 2.5 ppm / 5 ppm. Adjustable higher concentrations with internal dilution.
- Accuracy: ±2%
- Repeatability: ±2%
- Resolution: 0,001 ppm
- Analysis time: around 15 minutes
- Calibration: two point
- LED Wavelength: 550 nm
- Reagents consumption:
- Reagent 1: 2.25 ml / analysis – 1.75L / month
- Reagent 2: 4.55 ml / analysis – 3.30L / month
- Monthly consumption calculated assuming 1 analysis per hour.
-
Method – Colorimetric
After adding the sample into the measurement cell, some reagents are added in order to adjust the solution to the desired conditions (pH, valence’s elements, etc.). Then, a blank is done to correct any temperature or turbidity disturbance. Subsequently, a last reagent is added, and it reacts with solution developing a color, which is measured using a correct wavelength. Thanks to the photometer used, the result achieves a great accuracy.
Principle of measurement
Any ferric iron is reduced to the ferrous state by means of the hydroxylamine hydrochloride. The ferrous ions react with the 1:10-phenanthroline to form a pink complex when the buffer brings the solution within the range 5 to 7 pH.
Advantages of the method
The method enables iron to be measured at very rather higher levels without resulting in high absorbance values being obtained. The reagents are stable. If total iron has to be measured the stirring time may be increased to ensure that the iron has been completely dissolved by the acidic medium.
Specifications
- Range: From 0 to 2.5 ppm / 5 ppm. Adjustable higher concentrations with internal dilution.
- Accuracy: 2%
- Repeatability: 2%
- Resolution: 0,001 ppm
- Analysis time: around 15 minutes
- Calibration: two point
- LED Wavelength: 550 nm
- Reagents consumption:
- Reagent 1: 2.25 ml / analysis – 1.75L / month
- Reagent 2: 4.55 ml / analysis – 3.30L / month
- Monthly consumption calculated assuming 1 analysis per hour.
-
Method – Colorimetric
After adding the sample into the measurement cell, some reagents are added in order to adjust the solution to the desired conditions (pH, valence’s elements, etc.). Then, a blank is done to correct any temperature or turbidity disturbance. Subsequently, a last reagent is added, and it reacts with solution developing a color, which is measured using a correct wavelength. Thanks to the photometer used, the result achieves a great accuracy.
Principle of measurement
The method is the Standard method for the measurement of manganese in water and is based upon ISO Standard. The method involves the formation of the formaldoxime reagent, which reacts with manganese to form an orange-red complex. The manganese – formaldoxime complex is stable over the pH range of 3.5 to 10.5.
Advantages of the method
The method is specific for the measurement of manganese as the potential interference from the presence of iron, which forms a violet complex with formaldoxime, is removed by the addition of EDTA and hydroxylamine hydrochloride, which reduces the ferric iron to the ferrous state. The method actually is capable of measuring up to about 5 ppm of manganese.
Interferences
Iron (II), Cobalt (>1ppm), PO4 (<6ppm), total hardness (<300ppm)
Specifications
- Range: From 0 to 200 ppb / 500 ppb / 1000 ppb / 5ppm. Adjustable higher concentrations with internal dilution.
- Accuracy: 2%
- Repeatability: 2%
- Resolution: 0,1 ppb
- Analysis time: around 15 minutes
- Calibration: two point
- LED Wavelength: 450 nm
- Reagents consumption:
- Reagent 1: 0.5 ml / analysis – 0.5L / month
- Reagent 2: 0.5 ml / analysis – 0.5L / month
- Reagent 3 (interference eliminator): 0.5 ml / analysis – 0.5L / month
- Monthly consumption calculated assuming 1 analysis per hour.
-
Method – Colorimetric
After adding the sample into the measurement cell, some reagents are added in order to adjust the solution to the desired conditions (pH, valence’s elements, etc.). Then, a blank is done to correct any temperature or turbidity disturbance. Subsequently, a last reagent is added, and it reacts with solution developing a color, which is measured using a correct wavelength. Thanks to the photometer used, the result achieves a great accuracy.
Principle of measurement
An acetate buffer is used to achieve the optimal pH conditions in order Br-PADAP could react with Nickel, forming an intense pink color proportional to Nickel concentration.
Advantages of the method
The pink color that is formed could stain the measurement cell, interfering on the following analysis, but thanks to the cleaning solution used by the Instran, this possible interference is removed.
Interferences
Cobalt
Specifications
- Range: From 0 to 250 ppb / 500 ppb / 1000 ppb. Adjustable higher concentrations with internal dilution.
- Accuracy: 2%
- Repeatability: 2%
- Resolution: 0,1 ppb
- Analysis time: around 15 minutes
- Calibration: two point
- LED Wavelength: 545 nm
- Reagents consumption:
- Reagent 1: 0.45 ml / analysis – 0.4L / month
- Reagent 2: 4.5 ml / analysis – 3.25L / month
- Reagent 3: 1.35 ml / analysis – 1.0L / month
- Monthly consumption calculated assuming 1 analysis per hour.
-
Method – Colorimetric
After adding the sample into the measurement cell, some reagents are added in order to adjust the solution to the desired conditions (pH, valence’s elements, etc.). Then, a blank is done to correct any temperature or turbidity disturbance. Subsequently, a last reagent is added, and it reacts with solution developing a color, which is measured using a correct wavelength. Thanks to the photometer used, the result achieves a great accuracy.
Principle of measurement
The nitrate is reduced to nitrite in a basic medium. After that, nitrite is measured thanks to the diazatization reaction, forming a brightly colored diazo dye. The nitrite color development is proportional to the amount of nitrate. Due to this process, nitrite must be absent to use this method.
Advantages of the method
The reaction is extremely sensitive and a fairly high absorbance is obtained.
Interferences
Low concentrations of nitrite are already a high interference in the method.
Specifications
- Range: From 0 to 2ppm / 5ppm / 10ppm / 20ppm. Adjustable higher concentrations with internal dilution.
- Resolution: 2%
- Repeatability: 2%
- Analysis time: around 20 minutes
- Calibration: two point
- LED Wavelength: 540 nm
- Reagents consumption:
- Reagent 1: 1.8 ml / analysis – 1.5L / month
- Reagent 2: 8.1 ml / analysis – 6.0L / month
- Reagent 3: 2.7 ml / analysis – 2.0L / month
- Monthly consumption calculated assuming 1 analysis per hour.
-
Method – ISE
The standard known addition (SKA) technique is used to perform the analysis. During the process, two readings are done. The difference between both and the slope found during calibration are used to calculate the concentration. Possible changes on the matrix sample are corrected due to this both lectures, as the reference to calculate the result is the relative difference of mV and not the absolute values. This avoids external interferences.
Principle of measurement
Reagent 1 is added to activate the electrode before the analysis. After that, a first measurement is done. Subsequently, a small volume of a high concentrated nitrate solution is added. Finally, a second lecture of mV takes place to calculate the result. When the extracting solution is used, a cleaning solution of ammonia is needed after each analysis to eliminate cross-contamination.
Advantages of the method
Almost all probes are affected by nitrite and chloride interferences. However, an extracting solution is used at the beginning to eliminate totally the issues caused by these both ions, being thus NO3 ions the only ones that causes changes on the electrode.
Specifications
- Range: From 0 to 5ppm / 10ppm / 20ppm. Adjustable higher concentrations with internal dilution.
- Accuracy: 2%
- Repeatability: 2%
- Resolution: 0,01ppm or 0,1 ppm
- Analysis time: around 15 minutes
- Calibration: one point
- ISE: Nitrate NO3 electrode
- Reagents consumption:
- Reagent 1 (extracting solution): 2.5 ml / analysis – 2L / month
- Reagent 2: 2 ml / analysis – 1.5L / month
- Reagent 2: 2 ml / analysis – 1.5L / month
- Cleaning solution: 6 ml / analysis – 4.5L / month
- Monthly consumption calculated assuming 1 analysis per hour.
-
Method – Colorimetric
After adding the sample into the measurement cell, some reagents are added in order to adjust the solution to the desired conditions (pH, valence’s elements, etc.). Then, a blank is done to correct any temperature or turbidity disturbance. Subsequently, a last reagent is added, and it reacts with solution developing a color, which is measured using a correct wavelength. Thanks to the photometer used, the result achieves a great accuracy.
Principle of measurement
The method is based upon the diazotization reaction of the nitrous acid, formed from the nitrite ions, with the sulfanilamide to form a brightly colored diazo dye.
Advantages of the method
The method is specific for the measurement of nitrite ion as the nitrous acid has to be formed to achieve the diazotization reaction. The reaction is extremely sensitive and a fairly high absorbance is obtained for 100 ppb which is often the legal limit of nitrite in drinking water.
Specifications
- Range: From 0 to 100 ppb / 500 ppb. Adjustable higher concentrations with internal dilution.
- Accuracy: 2%
- Repeatability: 2%
- Resolution: 0,1 ppb
- Analysis time: around 15 minutes
- Calibration: two point
- LED Wavelength: 550 nm
- Reagents consumption:
- Reagent 1: 0.5 ml / analysis – 0.4L / month
- Reagent 2: 0.5 ml / analysis – 0.4L / month
- Monthly consumption calculated assuming 1 analysis per hour.
-
Method – Colorimetric
After adding the sample into the measurement cell, some reagents are added in order to adjust the solution to the desired conditions (pH, valence’s elements, etc.). Then, a blank is done to correct any temperature or turbidity disturbance. Subsequently, a last reagent is added, and it reacts with solution developing a color, which is measured using a correct wavelength. Thanks to the photometer used, the result achieves a great accuracy.
Principle of measurement
The method relies upon the reaction of the phenol with 4-aminoantipyrene followed by oxidation of the adduct with persulfate to form a pink complex.
Advantages of the method
The method is specific for phenol and all non-4-substituted monohydric phenols. The method is also very sensitive and levels as low as 0 to 100 ppb may be measured using the correct circumstances.
Specifications
- Range: From 0 to 100 ppb / 500 ppb / 1000 ppb. Adjustable higher concentrations with internal dilution.
- Accuracy: 2%
- Repeatability: 2%
- Resolution: 0,1 ppb
- Analysis time: around 15 minutes
- Calibration: two point
- LED Wavelength: 510 nm
- Reagents consumption:
- Reagent 1: 4 ml / analysis – 3.0L / month
- Reagent 2: 4 ml / analysis – 3.0L / month
- Monthly consumption calculated assuming 1 analysis per hour.
-
Method – Colorimetric
After adding the sample into the measurement cell, some reagents are added in order to adjust the solution to the desired conditions (pH, valence’s elements, etc.). Then, a blank is done to correct any temperature or turbidity disturbance. Subsequently, a last reagent is added, and it reacts with solution developing a color, which is measured using a correct wavelength. Thanks to the photometer used, the result achieves a great accuracy.
Principle of measurement
The method relies upon the direct reaction of phosphate ion to react with the Vanadomolybdate reagent to form a yellow colored complex.
Advantages of the method
The method appears to be specific for phosphate and is especially useful when measuring the higher concentrations of phosphate. Although the complex is yellow in color the autoblanking before the addition of the single reagent compensates for any background yellow color present in the sample. The other obvious advantage is that only a single reagent is used and the quantity of reagent added is very small (1 ml).
Specifications
- Range: From 0 to 2ppm / 5ppm / 10ppm / 20ppm / 60ppm. Adjustable higher concentrations with internal dilution.
- Accuracy: 2%
- Repeatability: 2%
- Resolution: 0,01 ppm
- Analysis time: around 10 minutes
- Calibration: two point
- LED Wavelength: 435 nm
- Reagents consumption:
- Reagent 1: 0.9 ml / analysis – 0.75L / month
- Monthly consumption calculated assuming 1 analysis per hour.
-
Method – Colorimetric
After adding the sample into the measurement cell, some reagents are added in order to adjust the solution to the desired conditions (pH, valence’s elements, etc.). Then, a blank is done to correct any temperature or turbidity disturbance. Subsequently, a last reagent is added, and it reacts with solution developing a color, which is measured using a correct wavelength. Thanks to the photometer used, the result achieves a great accuracy.
Principle of measurement
Ammonium molybdate and potassium antimonyl tartrate react in acid medium with orthophosphate to form a heteropoly acid-phosphomolybdic acid-that is reduced to intensely colored molybdenum blue by ascorbic acid.
Advantages of the method
The blue color developed is so intense and it provides a high accuracy and repeatability. The method allows to measure really low values of concentrations (lower than 50 ppb).
Interferences
Arsenates concentrations as low as 0.1 mg As/L interfere with the phosphate determination. Cr (VI) and NO2- interfere to give results about 3% low at concentrations of 1 mg/L and 10 to 15% low at 10 mg/L. Sulfide (Na2S) and silicate do not interfere at concentrations of 1.0 and 10 mg/L.
Specifications
- Range: From 0 to 200 ppb / 500 ppb / 1000 ppb
- Resolution: 2%
- Repeatability: 2%
- Analysis time: around 12 minutes
- Calibration: two point
- LED Wavelength: 810 nm
- Reagents consumption:
- Reagent 1: 0.5 ml / analysis – 0.5L / month
- Reagent 2: 0.5 ml / analysis – 0.5L / month
- Monthly consumption calculated assuming 1 analysis per hour.
-
Method – Colorimetric
After adding the sample into the measurement cell, some reagents are added in order to adjust the solution to the desired conditions (pH, valence’s elements, etc.). Then, a blank is done to correct any temperature or turbidity disturbance. Subsequently, a last reagent is added, and it reacts with solution developing a color, which is measured using a correct wavelength. Thanks to the photometer used, the result achieves a great accuracy.
Principle of measurement
Silica reacts with molybdate reagent in acid media to form a yellow silicomolybdate complex. This complex is reduced by ascorbic acid to form the molybdate blue color. The color intensity is proportional to the silica concentration.
Interferences
Phosphate and Tannin interferences can be removed thanks to oxalic acid. Hydrogen sulfide and large amounts of iron are also an interference.
Specifications
- Range: From 0 to 1 ppm / 5 ppm / 10 ppm. Adjustable higher concentrations with internal dilution.
- Resolution: 2%
- Repeatability: 2%
- Analysis time: around 15 minutes
- Calibration: two point
- LED Wavelength: 650 nm
- Reagents consumption:
- Reagent 1: 4 ml / analysis – 3L / month
- Reagent 2: 3 ml / analysis – 2.25L / month
- Reagent 3: 4 ml / analysis – 3L / month
- Monthly consumption calculated assuming 1 analysis per hour.
-
Method – Colorimetric
After adding the sample into the measurement cell, some reagents are added in order to adjust the solution to the desired conditions (pH, valence’s elements, etc.). Then, a blank is done to correct any temperature or turbidity disturbance. Subsequently, a last reagent is added, and it reacts with solution developing a color, which is measured using a correct wavelength. Thanks to the photometer used, the result achieves a great accuracy.
Principle of measurement
The initial reaction of the silica with the diammonium molybdate in such acidic conditions ensures that only the -molybdosilicic acid is formed. Then the solution is treated with tartaric acid to destroy the phosphomolybdic acid, which is formed under the same conditions. Finally, the molybdomolybdic acid is reduced to the molybdenum blue complex, which absorbs at 810 nm. If some of the -silicomolybdic acid is formed the molybdenum blue reduction product of this form absorbs at a lower wavelength, near to 730 nm. Hence, it is important to ensure that only the -isomer be formed in the initial stage.
Advantages of the method
Because only the -form of the silico-molybdic acid is formed the method has a fairly good sensitivity at the lower end as required by power plants and the electronics industry to ensure that the water is pure. The new formulation of Reagent #1 also speeds up the time required for the complete reaction. In addition, although the first reagent is relatively expensive very small volumes of reagent are required.
Specifications
- Range: From 0 to 100 ppb / 500 ppb (internal dilution)
- Resolution: 2%
- Repeatability: 2%
- Analysis time: around 15 minutes
- Calibration: two point
- LED Wavelength: 810 nm
- Reagents consumption:
- Reagent 1: 0.37 ml / analysis – 0.3L / month
- Reagent 2: 0.37 ml / analysis – 0.3L / month
- Reagent 3: 0.37 ml / analysis – 0.3L / month
- Monthly consumption calculated assuming 1 analysis per hour.
-
Method – ISE
The standard known addition (SKA) technique is used to perform the analysis. During the process, two readings are done. The difference between both and the slope found during calibration are used to calculate the concentration. Possible changes on the matrix sample are corrected due to this both lectures, as the reference to calculate the result is the relative difference of mV and not the absolute values. This avoids external interferences.
Principle of measurement
The sample is adjusted to pH between 8 to 11 thanks to Ion Strength Adjustor (ISA). After that, a first measurement is done. Subsequently, a small volume of a high concentrated sodium solution is added. Finally, a second lecture of mV is done to calculate the result.
Advantages of the method
The rapidly response of the electrode enables to perform a rapid analysis. The main cations that cause interferences are absent or significant low. Even this, ISA solution prevents these interferences.
Interferences
Lithium, Potassium, Rubidium, Ammonia, Silver, Thallium.
Specifications
- Range: From 0 to 500 ppb / 5 ppm / 20 ppm / 50 ppm. Adjustable higher concentrations with internal dilution.
- Accuracy: 2%
- Repeatability: 2%
- Resolution: 0,01 ppm or 0,1 ppm
- Analysis time: around 10 minutes
- Calibration: one point
- ISE: Sodium Na+ electrode
- Reagents consumption:
- Reagent 1: 1 ml / analysis – 1 L / month
- Reagent 2: 1 ml / analysis – 1 L / month
- Monthly consumption calculated assuming 1 analysis per hour.
Applications
Drinking water plants

Wastewater treatment plants

Chlor-alkali

Refineries

Power Plant - Cooling System

Automotive Industry

Desalination plants

Bicycle Gear Industry

Pure Water Control

About Us
At 80’s, Instrumentación Analítica was capable to develop our own laboratory equipment.
During 90’s, our multiple customers requested to spread out through different applications and analyzers, being Instrumentacion Analitica capable of adapting to the circumstances and demanding.
At the end of 2009, thanks to the experience of the owners and service team, with almost 30 years on activities, maintenances and knowledge provided by all the brands that Instrumentacion Analitica had distributed since the beginning, the ambitious project to develop and manufacturer an online analyzer started: INSTRAN was born.
Currently, more almost 15 years later, we are proud to say that Instrumentacion Analitica manufactures and distribute along the world, in cooperation with the best local companies, an analyzer that thanks to its accuracy, trustworthiness and service provided has achieved a significant reputation worldwide.
We have made Instran® an online analyzer with high analytical accuracy and low power consumption. Its advanced technology allows high accuracy in the operation with minimal consumption of reagents, thus reducing the environmental impact.
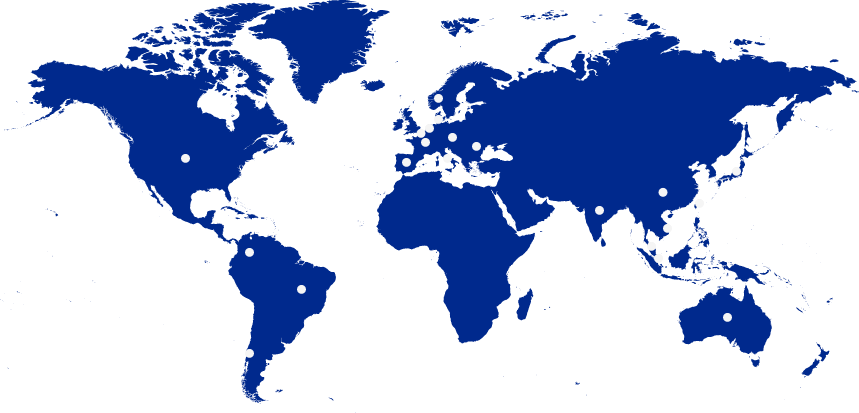
Worldwide
- Brazil
- United States
- Spain
- France
- Italy
- Norway
- Slovakia
- India
- China
- Taiwan
- Vietnam
- Malaysia
- Singapore
- Australia
- Chile
- Japan
- Netherlands
- Belgium
- Denmark
- Romania
- Colombia
Some of our clients










